
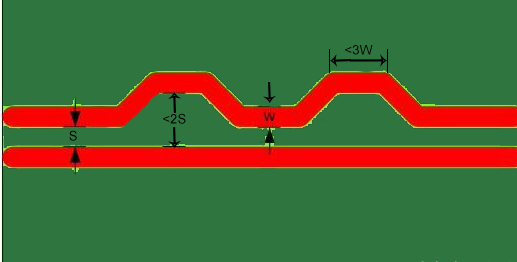
In the context of PCB design and manufacturing, the term "tight delay deviation" between positive and negative signals refers to the time difference in the transmission process between the two signals (positive and negative) of a differential signal pair. This deviation can affect the integrity of the signal, especially in high-speed data transmission, as it may lead to data errors or signal distortion.
To reduce this deviation, designers employ specific routing techniques, such as serpentine routing, which compensates for any length differences between two traces by adding extra path length. Carefully designed serpentine routing can reduce impedance discontinuities, thereby reducing delay deviation between signals. Impedance discontinuities refer to sudden changes in signal impedance due to variations in material or geometric shape along the signal transmission path, which can cause signal reflection and affect signal integrity.
In subsequent articles, we will introduce eight routing design schemes in detail, which aim to further reduce the tight delay deviation between positive and negative signals to enhance the performance and reliability of high-speed interfaces.