
Let's proceed to discuss the next attention point: Routing signals on a split plane should be avoided.
Incorrect signal return can lead to noise coupling and EMI issues. Designers should always consider the signal return path when routing signals. As shown in the cover diagram, contrary to this, the return current of high-speed signals attempts to follow the signal path.
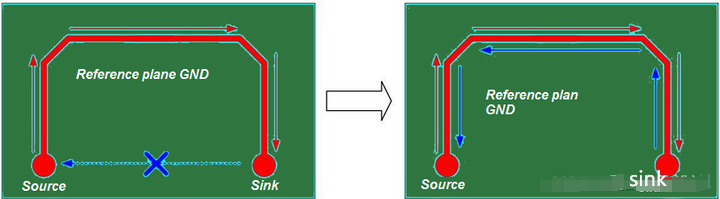
Signals should not be routed on a split plane because the return path cannot follow the signal trace. As illustrated in the following diagram, if a plane is separated into receive and source sections, signal traces need to be routed around it. If the forward and return paths of a signal are separated, the area between them will act as a loop antenna.
In the next article, we will discuss how to route signals on two different planes.