
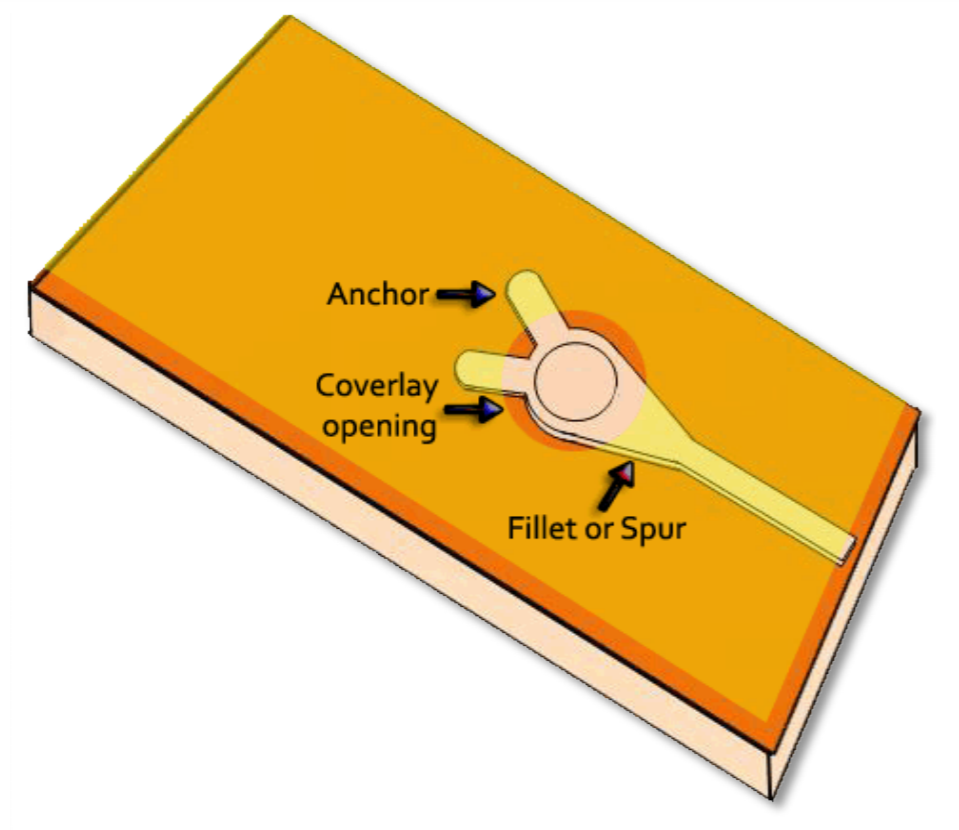
Flexible PCB Design Techniques
1. Enhance the reliability of flexible circuits:
During dynamic bending, the flexible sections undergo repeated bending and twisting, which can lead to delamination between the copper layers and the substrate material. To reduce this risk, use teardrops or crosshatch patterns on pads. Crosshatch patterns help stabilize the outer layers during dynamic bending, while teardrops can reduce or eliminate potential stress concentration points on the PCB. These designs not only strengthen pads and traces but also help prevent delamination. As shown in the cover image, crosshatch patterns and teardrops on flexible PCB traces and pads are effective methods to enhance reliability.
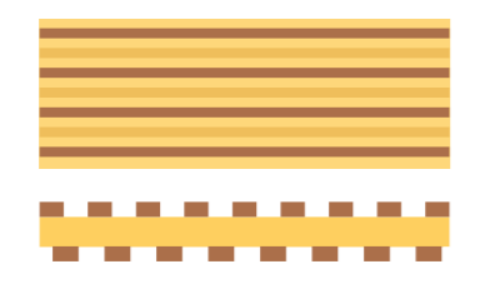
2. Staggered arrangement:
On double-sided flexible circuits, traces should be offset. Placing traces in the same position on both sides of a flexible circuit not only reduces the board's flexibility but also increases the stress on the copper traces. To evenly distribute stress, it is recommended to place flexible traces in a staggered manner, as shown in the figure below.
3. Avoid sharp corners on traces:
Sharp trace corners have more stress than straight lines, and straight lines can also reduce delamination issues. When changing the direction of a trace, it is advised to use smooth curved traces instead of sharp corners. This design can reduce stress concentration and improve the durability of the traces.

These are some solutions regarding rigid-flex PCB and flexible PCB design issues. If you are interested in learning more about rigid-flex PCB or need further information, you can contact our customer service personnel to place an order for a custom rigid-flex PCB.