
Continuing our discussion of medical and wearable device equipment PCB, today we will learn about how to overcome the difficulty of design medical and wearable device equipment PCB.
In the context of PCB production and manufacturing, "rigid-flex PCB design" refers to the technology of combining rigid and flexible materials in printed circuit boards (PCBs). This design is particularly suitable for electronic devices that need to bend or conform to irregularly shaped surfaces, such as wearable and medical devices. Since these devices may need to be attached to the human body, there are high demands for the flexibility and layout density of the PCB. Designers must cleverly arrange component positions and wiring to accommodate circular, elliptical, or irregularly shaped PCBs.
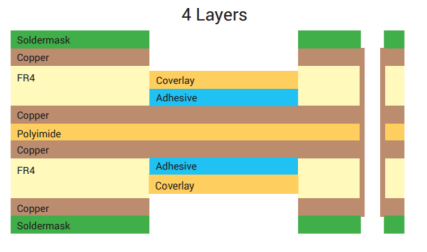
Rigid-flex PCBs allow designers to easily tackle these challenges by embedding flexible circuits between rigid boards. For example, a sample of a four-layer rigid-flex PCB may include two four-layer rigid boards connected by a single-layer flexible circuit. The number of layers and materials used in this design are crucial to performance.
In the next article, we will list another example of a rigid-flex PCB to illustrate how the design is carried out.