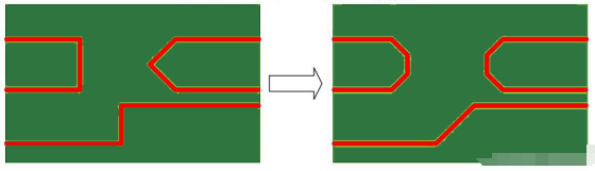
In the context of PCB manufacturing, routing high-speed signals requires special attention due to their sensitivity to the shape and layout of the traces. When bends are necessary in high-speed signal routing, it's best to avoid sharp 90° angles, as these acute corners can cause signal reflection and interference, acting much like antennas and thus affecting signal integrity.
Therefore, a 135° bend is recommended as it reduces signal interference and allows for a smoother transition during the PCB etching process. As shown in the cover image, a 135° bend is less abrupt than a 90° bend, which helps to minimize signal loss and reflection.
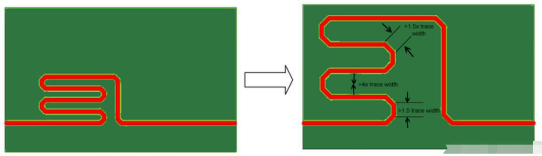
Sometimes, to achieve a specific trace length, serpentine routing may be necessary. In such cases, design rules dictate that the minimum distance between adjacent conductors in the same trace must be four times the trace width to prevent signal interference. Additionally, each bend segment should be 1.5 times the trace width to ensure that the signal remains stable through the bends. These design guidelines help maintain the stability and reliability of high-speed signals, ensuring the high performance of electronic devices.